Spring.AOP
1 面向切面编程 (AOP, Aspect Oriten Program)
如果对一个对象的方法进行 扩充 (不改变源码的情况之下,增加或修改行为)的话,一般使用代理模式:
静态代理(太麻烦,一般不会用)- JDK 的动态代理
- CGLib 的动态代理
但是,直接写代理生成太麻烦了,所以,基于动态代理,产生了 AOP 的编程思想。
扩充 = 功能分离。主线功能,支线功能,分开来,实现解耦。
实际中,基于代理实现的 AOP 方案有很多,比如:
- AspectJ 实现
- Jboss AOP 实现
- Spring AOP 实现
关于 Spring AOP:
- 默认情况下,它基于 JDK 动态代理,所以它需要有接口。
- 但是,也可以调用 CGLib 的代理方式。
- 一般情况下,要为一个类产生代理。如果它有接口,那么 Spring 会采取 JDK 动态代理方式;如果没接口,这时候它会尝试使用 CGLib 的方式产生代理
- Spring AOP 实现,它的功能 相对来说 比较弱,只能基于方法进行织入
- Spring AOP 压根就没有想过成为一个全能的 AOP 实现来取代 AspectJ,它主要的精力放在怎么跟容器结合起来更好用,怎么才能更好得配合企业级开发
- Spring AOP 借鉴了 AspectJ 的非常多的特性,比如说,Spring AOP 可以使用跟 AspectJ 完全一样的注解来声明切面。当然要明白,虽然我们可以使用 @AspectJ 的注解,但后面运行的还是实打实的 Spring AOP。
- Spring 中可以非常简单的将其他 AOP 的实现无缝整合到框架中,所以,如果你觉得 Spring AOP 的实现太逊,你完全可以将其他实现整合进来,取代 Spring AOP。
2 概念
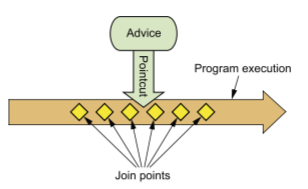
基本概念:
- Advice: 要向目标位置加入什么
- Pointcut: 要加到哪些位置
- Aspect: 一系列 Advice + Pointcut 的集合。
- Joinpoint: Pointcut 中的具体某个位置
织入(Weaving) 是把切面应用到目标对象并创建新的代理对象的过程:
- 编译期。切面在目标类编译时被织入。这需要特殊的编译器,比如 AspectJ
- 类加载期。需要特殊的 Classloader。AspectJ 的加载时织入就支持这种方式织入切面
- 运行期。使用动态代理的方式织入。Spring AOP 就是用这种方式织入的
通知类型:
- 前置通知(Before advice): 在某连接点之前执行的通知,但这个通知不能阻止连接点之前的执行流程(除非它抛出一个异常)
- 后置通知(After returning advice): 在某连接点正常完成后执行的通知
- 异常通知(After throwing advice): 在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知
- 最终通知(After (finally) advice): 当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。
- 环绕通知(Around Advice): 包围一个连接点的通知,如方法调用
3 使用 @AspectJ 注解实现
使用 @AspectJ 的注解,需要相关 jar 包支持:
org.aspectj:aspectjweaver:1.8.9
而且需要在配置文件中添加:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/> <!-- cglib support --> <!-- or --> <bean class="org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator"/>
如果使用 Java 配置,需要添加:
@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "the.aop") @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class SpringConfig { }
代码示例:
@Component @Aspect public class Audience { @Pointcut("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void xxx(); @Before("xxx()") public void silenceCellPhones() { System.out.println("Silencing cell phones"); } @Before("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void takeSeats() { System.out.println("Taking seats"); } @AfterReturning("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void applause() { System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP!!!"); } @AfterThrowing("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void demandRefund() { System.out.println("Demanding a refund"); } @Around("xxx()") public Object yyyy(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) { Object ret = null; try { System.out.println("aaaa"); ret = jp.proceed(); System.out.println("bbb"); } catch(Throwable e) { System.out.println("error"); } return ret; } }
切点表达式:
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| execution() | execution(* com.*.*(..)), 表示匹配 com 包下所有方法 |
| @annotation() | @annotation(com.Test), 表示匹配所有标注了 @Test 的方法 |
| args() | arg(int, int), 表示匹配所有参数为 int, int 的方法 |
| @args() | @arg(Test), 匹配参数注解为 Test 的方法 |
| within() | within(sss.*), 匹配 sss 包下所有的类下的所有方法 |
| target() | target(sss.Test), 匹配所有的类及其子类 |
| @within() | @within(sss.Test), 匹配所有使用 Test 注解的类的所有方法 |
| @target | @target(sss.Test), 所有当前目标对象使用 Test 注解的类的所有方法 |
| this() | this(sss.Test), 当前 AOP 对象实现了 Test 接口的所有方法 |
4 使用 XML 配置的方式实现
<aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="loggingAspect"> <!-- 切面类 --> <aop:pointcut id="persons" expression="execution(* xxx.*.*(..))" /> <!-- 切点 --> <aop:before method="beforeEat" pointcut-ref="persons" /> <aop:after-returning method="endIt" pointcut-ref="persons" /> <aop:after-throwing method="whenError" pointcut-ref="execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))" /> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
5 声明式事务管理
这是 AOP 的一种典型运用场景:
5.1 XML Style
<!--1.配置事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" /> <!--2.配置通知--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="get*" timeout="1000" isolation="READ_COMMITTED" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="save*" read-only="false" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!--3.将通知切入到相应位置--> <aop:config> <!--<aop:pointcut id="dbOp" expression="execution(* the.jdbc_aop.*(..))" />--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* the.jdbc_aop.*(..))" /> </aop:config>
5.2 @Transactional Style
首先,开启注解支持:
<!--1.配置事务管理器--> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" /> <!--2.启用注解--> <tx:annotation-driven proxy-target-class="true" />
其次,就可以使用 @Transactional 注解了:
@Service @Transactional(readOnly = true) public class GoodServcie { @Transactional(timeout = 1000, readOnly = false) public void saveGood(String good) { // 1. 保存日志 // 2. 查询货物状态 // 3. 保存货物 } public void lingwaiyige() { } }
一般加在 Service 层上。